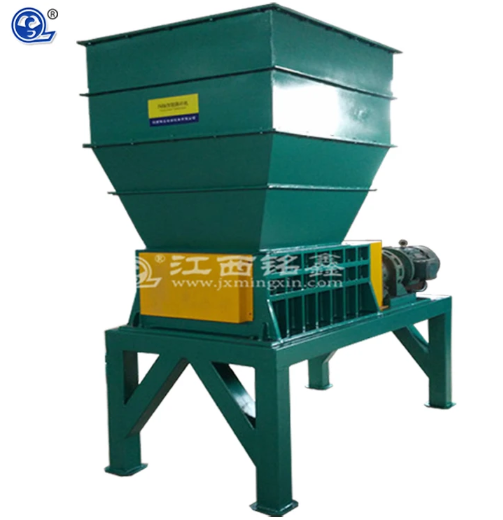
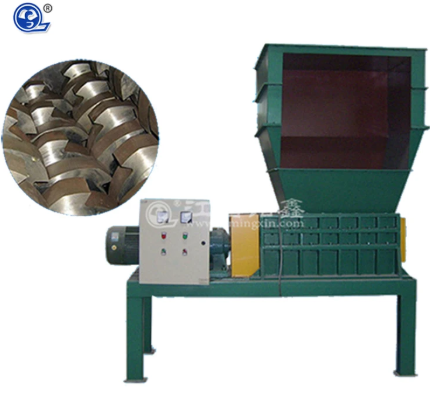


The four-shaft shredder is an efficient solid waste disposal equipment primarily used for shredding tough and resilient waste materials such as metal drums, waste tires, rigid plastics, car bodies, and discarded household appliances.
Working Principle
Cutting and Shredding: The four-shaft shredder is equipped with four sets of rotors fitted with blades, driven by a reducer to rotate the main shaft under the fixed action of the machine body. When materials enter the crushing chamber, larger pieces are first secured and coarsely crushed by the upper two sets of rotors. The fixed and drawn-in materials are then forcibly shredded by the bottom rotors. Through the combined actions of tearing, shearing, and squeezing by the four sets of blades, the materials are broken down into smaller pieces.
Particle Screening: After the materials are crushed, those with dimensions smaller than the screen mesh openings are discharged from the bottom screen openings of the box under the action of gravity and pressure. Larger materials remain in the crushing chamber for further shredding until their dimensions are smaller than the screen mesh openings.
Structural Components
Shredding Blade Sets: The core component of the shredder, typically divided into stationary blades and moving blades. The stationary blades are fixed to the shredder’s main shaft via internal hexagonal positioning holes, while the moving blades are mounted on the rotors. The blades are generally made of imported alloy steel, offering high wear resistance, moderate toughness, strong interchangeability, and a long service life.
Main Shaft: Usually a regular hexagonal cross-section shaft, connected to the reducer via bearings and couplings. It provides support for bearing installation and shaft fixation while creating a relatively enclosed space for the four-shaft联动 crushing. The internal pressure-bearing cylinder reduces friction during shaft rotation, thereby minimizing torque loss.
Carrying Box and Box Support: The carrying box is where material crushing takes place, typically welded or cast from high-wear-resistant steel. It offers high strength and wear resistance, capable of withstanding the impact forces during the crushing process. The box support is used to hold the carrying box, ensuring the stability of the equipment.
Feeding System: Responsible for transporting materials to be crushed into the shredder’s crushing chamber. Different feeding devices, such as conveyor belts or screw feeders, can be equipped based on actual needs.
Power System: Includes the motor, reducer, and couplings, providing the driving force for the shredder’s operation. The motor adjusts the output speed through the reducer while increasing the torque of the main shaft, enabling the blade shafts to operate at low speeds and high torque for efficient crushing.
Electrical Control System: Typically uses a programmable logic controller (PLC) as the main controller. It controls the rapid closing of the motor and hydraulic system via AC contactors and solenoid directional valves and integrates a synchronous speed regulation system to effectively ensure the synchronization of the four shafts. Additionally, it features functions such as one-button start/stop, status monitoring, data analysis, collaborative optimization, fault diagnosis, and alarm linkage.
Performance Characteristics
Powerful Crushing Capability: The four blade shafts work in coordination, offering stronger gripping and shearing capabilities. This enables forceful crushing of highly resilient and ductile materials such as metal, rubber, and rigid plastics. Compared to dual-shaft shredders, it provides a larger crushing ratio and can handle more difficult-to-shred materials.
High Efficiency and Energy Saving: The unique blade shaft structure and blade tooth shape reduce ineffective material grabbing, reversal, and idling time, improving crushing efficiency and lowering energy consumption. Additionally, the low-speed, high-torque power system design makes the equipment more energy-efficient during operation.
Controllable Output Size: By equipping the discharge outlet with quickly replaceable screens, users can flexibly control the final crushing size of the materials according to actual needs, ensuring uniform particle size.
Stable and Reliable Operation: The use of internationally renowned bearing brands, along with quadruple sealing, effectively prevents interference from sewage, sludge, and dust, extending the service life of the bearings. Furthermore, the rational design of the equipment body, combined with appropriate heat treatment processes, enhances the overall performance of components such as the blade box, making them less prone to deformation over prolonged use.
Easy Operation and Maintenance: The intelligent monitoring system helps customers accurately grasp the equipment’s operating status in real time, facilitating timely problem detection and resolution. Additionally, worn blades can be repaired using techniques such as coating welding, allowing for multiple reuses and significantly reducing blade maintenance costs.
Application Fields
Solid Waste Treatment Industry: Can be used to process household waste, industrial waste, bulky waste, etc., shredding various solid wastes into smaller particles for subsequent sorting, recycling, and treatment.
Resource Recycling: Suitable for the recycling and processing of waste metals, plastics, rubber, paper, and other resources. Through the shredding action, these waste resources are preliminarily processed for subsequent reuse, such as metal smelting and plastic pelletizing.
Electronic Waste Treatment: Capable of shredding waste electrical appliances and electronic products such as refrigerators, television casings, and circuit boards. This aids in separating different materials like metals and plastics, achieving harmless treatment and resource recovery of electronic waste.
Automotive Dismantling Industry: Used for shredding automotive components such as car bodies, tires, and bumpers, breaking them into small pieces for subsequent metal recovery and other processing steps.
Specification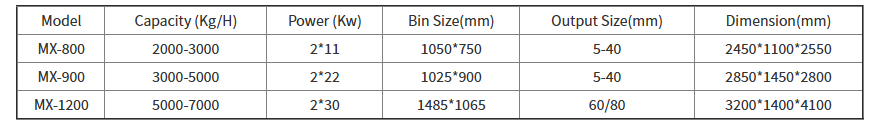

 four shaft shredder-Recycling Product-Jiangxi Mingxin Metallurgical Equipment Co., Ltd.
four shaft shredder-Recycling Product-Jiangxi Mingxin Metallurgical Equipment Co., Ltd.